Spirochaetal Diseases of Human
Abstract
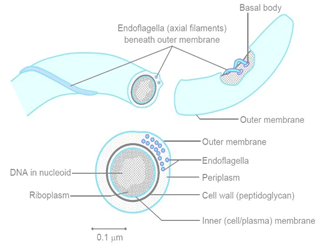
Spirochetes are a Group of gram-negative bacteria having spiral shape structures. They are highly pathogenic. These bacteria are unique and comprise endocellular flagella ranging from 2 to above 100 per organism. Pathogenic species of spirochetes cause diseases such as syphilis and Lyme disease. Treponema pallidum causes syphilis. In addition, they usually cause sexually transmitted diseases. The symptoms include skin sores, bone lumps, skin growth, and discoloration patch. Penicillin injection is used to get rid of them. Borrelia has 52 species that cause borreliosis, also called Lyme disease and relapsing fever. They spread through lice and ticks. The symptoms include fever, chills, headache, nausea, and rashes. Moreover, Leptospira causes leptospirosis, also called Weil’s disease. It includes flu-like symptoms. It can also exhibit meningitis and lung bleeding in severe cases. Spirochetes can be found in a diverse range of environments. They are both parasitic and free living. They are very tough to culture. They are usually 5-50 μm in length. Morphological characteristics of spirochetes are: Outer membrane, Periplasmic space containing flagella, Peptidoglycan layer, Endoflagella, Inner cytoplasmic membrane. Spirochetes can be easily differentiated among other Gram-negative bacteria because of the unique endoflagella, which imparts motility. Flagella winds around the shape of bacteria between the cell wall and outer membrane. This structure is called the axial filament. When the axial filament rotates, spirochetes move in a spiral motion.
Full text article
References
Araujo, ER. “Acute Kidney Injury in human leptospirosis: an immunohistochemical study with pathophysiological correlation”. vol. 456. (2019). pp. 367-37.Association of genetic variability within the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato with the ecology, epidemiology of Lyme borreliosis in Europe. Derdáková M, Lencáková D. 2020., Ann Agric Environ Med, pp.: 12(2):165-72.
Barbour AG. (2018). Borreliaceae. In Whitman WB, Rainey F, Kämpfer P, Trujillo M, Chun J, DeVos P, Hedlund B, Dedysh S (ed), Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. Wiley, New York, NY.
Beranard Roizman. Infectious Diseases in an Age of Change: The Impact of Human Ecology and Behavior on Disease Transmission. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2020.
Bharti, AR. “Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance”. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. vol. 3. 2021. pp. 757-771.
Brett-Major, DM. “Antibiotic prophylaxis for leptospirosis”. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews online. 2022.
Brodsky JL, Samuel MC, Mohle-Boetani JC, et al. Syphilis outbreak at a California men's prison, 2007-2018: propagation by lapses in clinical management, case management, and public health surveillance. J Correct Health Care. 2018;19(1):54–64.
Buchacz K, Patel P, Taylor M, et al. Syphilis increases HIV viral load and decreases CD4 cell counts in HIV-infected patients with new syphilis infections. Aids. 2019;18(15):2075–9.
Calonge N., U. S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for syphilis infection: recommendation statement. Ann Fam Med. 2019;2(4):362–5. [Erratum appears in Ann Fam Med. 2019Sep-Oct;2(5):517
Dellagostin, OA. “Recombinant vaccines against Leptospirosis”. Human Vaccines. vol. 7. 2018. pp. 1215-1224.
Dolan MC, Breuner NE, Hojgaard A, Boegler KA, Hoxmeier JC, Replogle AJ, Eisen L. Transmission of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia mayonii in relation to duration of attachment by nymphal Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2019:54(5):1360-4.
Dolan MC, Breuner NE, Hojgaard A, Boegler KA, Hoxmeier JC, Replogle AJ, Eisen L. Transmission of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia mayonii in relation to duration of attachment by nymphal Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2017:54(5):1360-4.
Duerr STK, Mowry S, Pfister A, LaDeau SL, Ostfeld RS. Assessing effectiveness of recommended residential yard management measures against ticks. J Med Entomol 2019:56(5):1420-27.
Eldin C, Raffetin A, Bouiller K, Hansmann Y, Roblot F, Raoult D, Parola P. Review of European and American guidelines for the diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. Med Mal Infect. 2019:49(2):121-32.
Englekens, HJ, Vuzevski, VD, Stolz, E. “Non-venereal treponematoses in tropical countries”. Clinics in Dermatology. vol. 17. 2020. pp. 143-152.
Evangelista, KV, Coburn, J. “Leptospira as an emerging pathogen: a review of its biology, pathogeneisis and host immune responses”. Future Microbiology. vol. 5. 2019. Pp.
Forrai J, compiler. In: History of Different Therapeutics of Venereal Disease Before the Discovery of Penicillin,Syphilis - Recognition, Description and Diagnosis. Dr. Neuza Satomi Sato; 2020. [Google Scholar].
Fritz CL, Kjemtrup AM. Lyme borreliosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2018:223:1261-70.
Gabitzsch ES. Piesman J. Dolan MC, Sykes CM, Zeidner NS. Transfer of Borrelia burgdorferi s.s. infection via blood transfusion in a murine model. J Parasitol. 2021;92(4):869-70.
Gall Y, Pfister K. Survey on the subject of equine Lyme borreliosis. Int J Med Microbiol. 2020;296 Suppl 40:274-9.
Gerber B. Haug K, Eichenberger S, Reusch CE, Wittenbrink MM.Follow-up of Bernese Mountain dogs and other dogs with serologically diagnosed Borrelia burgdorferi infection: whathappens to seropositive animals? BMC Vet Res. 2018;5:18.
Ghanem KG, Hook EW. Syphilis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 303.
Gjestland T. The Oslo study of untreated syphilis; an epidemiologic investigation of the natural course of the syphilitic infection based upon a re-study of the Boeck-Bruusgaard material. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 2021;35(Suppl 34):3–368. Annex I-LVI.
Global analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi genes regulated by mammalian host-specific signals. Brooks CS, Hefty PS, Jolliff SE, Akins DR. 2018., Infect Immun., pp.: 71(6):3371-83.
Izard J, Renken C, Hsieh CE, Desrosiers DC, Dunham-Ems S, La Vake C, Gebhardt LL, Limberger RJ, Cox DL, Marko M, Radolf JD. 2019
Jarrell K.F., McBride M.J. The surprisingly diverse ways that prokaryotes move. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2019;6:466–476. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1900. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar].
Jordan BE, Onks KR, Hamilton SW, Hayslette SE, Wright SM. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia lonestari in birds in Tennessee. J Med Entomol. 2019;46(1):131-8.
Katz, AR, Buchholz, AE, Hinson, K, Park, SY, Effler, PV. “Leptospirosis in Hawaii, USA. Emerging Infectious Diseases. vol. 17. 2018. pp. 221-226.
Kudryashev M, Cyrklaff M, Baumeister W, Simon MM, Wallich R, Frischknecht F. 2020. Comparative cryo-electron tomography of pathogenic Lyme disease spirochetes. Mol Microbiol 71:1415–1434.
Lo, Y, Kintziger, KW, Carson, JH, Patrick, SL, Turabelidze, G, Stanek, D, Blackmore, C, Lingamfelter, D, Dudley, MH, Shadomy, SV, Shieh, W, Drew, CP, Batten, BC, Zaki, SR. “Severe Leptospirosis Similar to Pandemic (H1N1) 2020, Florida and Missouri, USA”. Emerging Infectious Diseases. vol. 17. 2011. pp. 1145-1146.
Marx R, Aral SO, Rolfs RT, et al. Crack, sex, and STD. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;18(2):92–101. [PubMed].
Mayer KH, Bush T, Henry K, et al. Ongoing sexually transmitted disease acquisition and risk-taking behavior among US HIV-infected patients in primary care: implications for prevention interventions. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;39(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed].
Miyata M., Robinson R.C., Uyeda T.Q.P., Fukumori Y., Fukushima S., Haruta S., Homma M., Inaba K., Ito M., Kaito C., et al. Tree of motility – A proposed history of motility systems in the tree of life. Genes Cells. 2020;25:6–21.
Moore MB Jr., Price EV, Knox JM, et al. EPIDEMIOLOGIC TREATMENT OF CONTACTS TO INFECTIOUS SYPHILIS. Public health reports. 2021;78:966–70.
Nelson HD, Glass N, Huffman L, et al. Screening for syphilis: brief update for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2020.
Owusu-Edusei K Jr., Chesson HW, Gift TL, et al. The estimated direct medical cost of selected sexually transmitted infections in the United States, 2008. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;40(3):197–201. [PubMed].
Palacios R, Jimenez-Onate F, Aguilar M, et al. Impact of syphilis infection on HIV viral load and CD4 cell counts in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020;44(3):356–9. [PubMed].
Palaniappan, R. “Leptospirosis: pathogenesis, immunity, and diagnosis”. Current Opinion in Infectiouis Diseases. vol. 20. 2020. pp. 284-292.
Pappas G. “The globalization of leptospirosis: worldwide incidence trends”. International Journal of Infectious Diseases. vol. 12. 2017. pp. 351-357.
Radolf JD, Caimano MJ, Stevenson B, Hu LT. Of ticks, mice and men: understanding the dual-host lifestyle of Lyme disease spirochaetes. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;10(2):87–99.
Radolf JD, Tramont EC, Salazar JC. Syphilis (Treponema pallidum). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020
Rogers EA, Terekhova D, Zhang HM, Hovis KM, Schwartz I, Marconi RT. Rrp1, a cyclic-di-GMP-producing response regulator, is an important regulator of Borrelia burgdorferi core cellular functions. Mol Microbiol. 2019;71(6):1551–73.
Rudenko N. A divergent spirochete strain isolated from a resident of the southeastern United States was identified by multilocus sequence typing as Borrelia bissettii. Parasit Vectors. 2020;9:68.
Samuels DS. Gene regulation in Borrelia burgdorferi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2021;65:479–99. Schroeter AL, Turner RH, Lucas JB, et al. Therapy for incubating syphilis. Effectiveness of gonorrhea treatment. JAMA. 2018;218(5):711–3. [PubMed]
Shah BB, Lang AE. Acquired neurosyphilis presenting as movement disorders. Mov Disord. 2019;27(6):690–5. [PubMed].
Spiteri G, Unemo M, Mårdh O, Amato- Gauci AJ. The resurgence of syphilis in high-income countries in the 2000s: a focus on Europe. Epidemiol Infect 2019;147:e143.
Stary G, Stary A. Sexually transmitted infections. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 82.
Sultan SZ, Pitzer JE, Miller MR, Motaleb MA. Analysis of a Borrelia burgdorferi phosphodiesterase demonstrates a role for cyclic-di-guanosine monophosphate in motility and virulence. Mol Microbiol. 2018;77(1):128–42.
T. Gardner R, Levine R, Scherrer N, Tewari D, Tomlinson J. Johnson AL, Retrospective evaluation of horses diagnosed with neuroborreliosis on postmortem examination: 16 cases (2004-2015). J Vet Intern Med. 2016;30(4):1305-12.
Takabe K., Tahara H., Islam M.S., Affroze S., Kudo S., Nakamura S. Viscosity-dependent variations in the cell shape and swimming manner of Leptospira. Microbiology. 2020;163:153–160.
Tao Y, Chen MY, Tucker JD, et al. A nationwide spatiotemporal analysis of syphilis over 21 years and implications for prevention and control in China. Clin In- fect Dis 2020;70:136-9.
Tilly K, Krum JG, Bestor A, Jewett MW, Grimm D, Bueschel D, Byram R, Dorward D, Stewart P, Rosa P. Borrelia burgdorferi OspC protein required exclusively in a crucial early stage of mammalian infection. Infect Immun. 2020;74(6):3554–64.
Van Wagoner NJ, Harbison HS, Drewry J, et al. Characteristics of women reporting multiple recent sex partners presenting to a sexually transmitted disease clinic for care. Sex Transm Dis. 2020;38(3):210–5. [PubMed].
Vidotto O, de Freitas JC, Vieira ML. First record of Borrelia burgdorferi B31 strain in Dermacentor nitens ticks in the northern region of Parana (Brazil). Braz J Microbiol. 2019:44(3):883-7.
Weinstock H, Berman S, Cates W Jr. Sexually transmitted diseases among American youth: incidence and prevalence estimates, 2018. Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2020;36(1):6–10. [PubMed].
Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2017. MMWR Recommendations and reports : Morbidity and mortality weekly report Recommendations and reports / Centers for Disease Control. 2017;64(RR-03):1–137.