Prednisolone Induced Exogenous Cushing Syndrome: A Case Report
Abstract
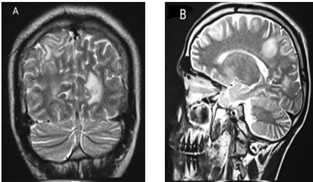
Exogenous Cushing syndrome (ECF) develops when a patient uses synthetic (man-made) glucocorticoids to treat a condition. These drugs have cortisol-like effects on the body. ECS may be caused by oral corticosteroids such as cortisone or prednisone. In an adult, CS can appear as proximal muscular weakness, facial plethora, wasting of the extremities along with higher fat in the abdominal region and face, wide reddish striae, bruising without evident trauma, and supraclavicular fat deposits. In this case report, a 39-year-old woman was suspected of having Cushing syndrome because of his clinical symptoms and low cortisol levels due to taking oral corticosteroids for the last 2 years. She presented weakness, joint pain, buffalo hump, skin infection, diabetes mellitus type-2, along with suspicion of Central hypothyroidism. MRI scan of the brain showed demyelinating lesions. After a physical examination and laboratory data confirmed that the patient was diagnosed with corticosteroid-induced exogenous Cushing syndrome.
Full text article
References
Brzozowska MM, Kepreotis S, Tsang F, Fuentes-Patarroyo SX. Improvement in cognitive impairment following the successful treatment of endogenous Cushing’s syndrome-a case report and literature review. BMC Endocrine Disorders. 2019;19:1-9.
Wannachalee T, Jantanapornchai N, Suphadirekkul K, Sirinvaravong S, Owattanapanich W. Multiple myeloma concealed by adrenal Cushing syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Medical Case Reports. 2018;12(1):1-5.
Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, Montori VM. The diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2008;93(5):1526-40.
Zhang D, Jiang Y, Lu L, Lu Z, Xia W, Xing X, Fan H. Cushing’s Syndrome With Nocardiosis: A Case Report and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2021;12:640998..
Laws Jr ER. Neurosurgery’s man of the century: Harvey Cushing—the man and his legacy. Neurosurgery. 1999;45(5):977.
Prague JK, May S, Whitelaw BC. Cushing’s syndrome. Bmj. 2013;346.
Nieman LK. Diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome in the modern era. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics. 2018 Jun 1;47(2):259-73.
Eviz E, Mutlu GY, Akcay AA, Erbey F, Guran T, Hatun S. An Overlooked Manifestation of Hypercortisolism-Cerebral Cortical Atrophy and Challenges in Identifying the Etiology of Hypercortisolism: A Report of 2 Pediatric Cases. Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 2023:1-.
Shaver D. Case report: Patient presenting with Cushing's disease. Surgical Neurology International. 2015;6(Suppl 6):S268.
Sıklar Z, Bostanci I, Atli O, et al. An infantile Cushing syndrome due to misuse of topical steroid. Pediatr Dermatol 2004;21:561–3.
Hengge UR, Ruzicka T, Schwartz RA, et al. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticoids. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006; 54:1–15.
Robertson DB, Maibach HI. Adverse systemic effects of TCS. In Maibach HI, Surber C, editors. TCS. Basel: Karger; 1992:pp. 163–169.
De Wachter E, Vanbesien J, De Schutter I, et al. Rapidly developing Cushing’s syndrome in a 4-year-old patient during combined treatment with itraconazole and inhaled budesonide. Eur J Pediatr 2003;162:488–9.
Anderson Jr GH, Blakeman N, Streeten DH. The effect of age on prevalence of secondary forms of hypertension in 4429 consecutively referred patients. Journal of hypertension. 1994;12(5):609.
Catargi B, Rigalleau V, Poussin A, Ronci-Chaix N, Bex V, Vergnot V, Gin H, Roger P, Tabarin A. Occult Cushing’s syndrome in type-2 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003;88(12):5808-13.
Chiodini I, Torlontano M, Scillitani A, Arosio M, Bacci S, Di Lembo S, Epaminonda P, Augello G, Enrini R, Ambrosi B, Adda G. Association of subclinical hypercortisolism with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case-control study in hospitalized patients. European journal of endocrinology. 2005;153(6):837-44.
Chiodini I, Mascia ML, Muscarella S, Battista C, Minisola S, Arosio M, Santini SA, Guglielmi G, Carnevale V, Scillitani A. Subclinical hypercortisolism among outpatients referred for osteoporosis. Annals of internal medicine. 2007;147(8):541-8.
Azzoug S, Rabehi L, Hannachi S, Medjdoubi H, Chentli F. Cushing [apos] s syndrome and hypertension. InEndocrine Abstracts 2015 May 1 (Vol. 37). Bioscientifica.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.