Exploratory-Data and Statistical Analyses of AB070597, an Amino Acid/Peptide Complex, on Blood-Serum Creatinine Concentration and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate: A Non-Randomized Pilot Trial of Five Humans with Declining Renal Function
Abstract
Background:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) develops from persistent, irremediable loss of renal function (RF). Animal studies show that dietary supplement, AB070597, an amino acid/ peptide complex, can stabilize, and in some instances, reverse CKD. Previous human CKD studies demonstrate that dietary treatment with specific keto acids and amino acids can lower blood-serum creatinine concentration (SCr) and increase glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This pilot trial was performed to determine whether a future randomized controlled human clinical trial of AB070597’s effect on CKD was justified.
Methods:
The trial was structured as a consecutive case series to evaluate whether oral treatment with AB070597 could slow CKD progression, as gaged by SCr, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Eligibility requirements: Non-diabetic white males under current medical care in the United States, diagnosed with CKD, or with histories of increasing SCr and declining eGFR, resulting from CKD or natural consequence of aging. Exclusion criteria: Concurrent or suspected comorbidities unrelated to CKD. Participants ingested 6-g bi-daily doses of AB070597 for periods up to 24 months. SCr was measured and eGFR calculated at approximate tri-monthly intervals.
Results:
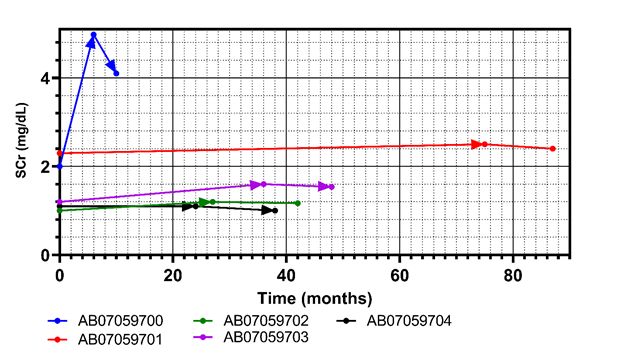
Results were presented as individual-participant and group SCr and eGFR vectors, and initial-data-analysis diagrams.
Treatment reversed SCr slopes from positive to negative, and eGFR slopes from negative to positive. When individual participant’s median monthly eGFR rate-of-change (positive) was compared with the median monthly eGFR rate-of-change (negative) in a sample of 2870 humans with CKD, differences were significant in favor of the AB070597 treatment group in 4 of 5 participants: (P = 0.0625, 95% CI: 0.368-8.368), (P = 0.0313, 95% CI: 0.368-1.038), (P = 0.0039, 95% CI: 0.368-0.698), (P = 0.0010, 95% CI: 0.118-2.868),
(P <0.0001, 95% CI: 0.368-10.370).
Conclusion:
Oral AB070597 treatment produced an apparently favorable change in CKD trajectory in 4 humans and in 1 with naturally age-related declining RF. The magnitude and direction of change hint that treatment may have had a beneficial effect on CKD progression and age-related RF. In and of themselves, this pilot trial’s results seem to favor CKD treatment with AB070597, but because there was no randomization, no control group, and a small sample size , it is not possible to extend results beyond its bounds. They do, however, support the rationale for a future randomized controlled trial
Full text article
References
[2]. Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States (2019) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2019. http://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/publications-resources/2019-national-facts.html. Accessed 16 Jul 2019
[3]. Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007;298(17):2038-47.
[4]. Cohen E, Nardi Y, Krause I, Goldberg E, Milo G, Garty M, et al. A longitudinal assessment of the natural rate of decline in renal function with age. J Nephrol 2014;27(6):635-41.
[5]. Ceballos I, Chauveau P, Guerin V, Bardet J, Parvy P, Kamoun P, et al. Early alterations of plasma free amino acids in chronic renal failure. Clin Chim Acta 1990;188(2):101-8.
[6]. Kumar VS, Kumar BS, Kishore Babu S, Kumar TS, Sathya Sai RN, Soloman A, Kumar KA. Serum amino acid profile in chronic renal failure. Indian Journal of Nephrology 1998;Apr-Jun 8(2):52-4.
[7.] Tizianello A, De Ferrari G, Garibotto G, Gurreri G, Robaudo C. Renal metabolism of amino acids and ammonia in subjects with normal renal function and in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Clin Invest 1980; 65(5):1162-73.
[8.] Cobo M, Martin Gomez MA, Frutos MA, Benavides M. Glutamin concentrations in patients treated with cisplatin have a predicting value of renal failure development. Nefrologia 2007; 27(1):23-9.
[9.] Watanabe M, Suliman ME, Qureshi AR, Garcia-Lopez E, Barany P, Heimburger O, et al. Consequences of low plasma histindine in chronic kidney disease patients: associations with inflammation, oxidative stress, and mortality. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87:1860-6.
[10.] Suliman ME, Qureshi AR, Stenvinkel P, Pecoits-Filho R, Barany P, Heimburger O, et al. Inflammation contributes to low plasma amino acid concentrations in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82(2):342-9.
[11.] Bergstrom J, Furst P, Noree LO, Vinnars E. Intracellular free amino acids in muscle tissue of patients with chronic uraemia: effect of peritoneal dialysis and infusion of essential amino acids. Clin Sci Mol Med 1978; 54(1):51-60.
[12.] Mitch WE, Walser M, Steinman TI, Hill S, Zeger S, Tungsanga K. The effect of a keto acid-amino acid supplement to a restricted diet on the progression of chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med 1984; 311(10):623-9.
[13.] Yatzidis H. Oral supplement of six selective amino acids arrest progression renal failure in uremic patients. Int Urol Nephrol 2004; 36(4):591-8.
[14.] Smoyer WE, Brouhard BH, Rassin DK, LaGrone L. Enhanced GFR response to oral versus intravenous arginine administration in normal adults. J Lab Clin Med 1991; 118(2):166-75.
[15.] Ito-Kato E, Suzuki N, Maeno M, Takada T, Tanabe N, Takayama T, et al. Effect of carnosine on runt-related transcription factor-2/core binding factor alpha-1 and Sox9 expressions of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res 2004; 39(3):199-204.
[16.] Zeisberg M, Hanai J, Sugimoto H, Mammoto T, Charytan D, Strutz F, et al. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat Med 2003; 9(7):964-8.
[17.] Archer J. Effect of renoprotective amino acids and a dipeptide on disease progression, nutritional status, and blood-serum phosphate concentration in cats with chronic kidney disease. Research Journal for Veterinary Practitioners 2019; 7(2):39-52.
[18.] Park YJ, Volpe SL, Decker EA. Quantitation of carnosine in humans plasma after dietary consumption of beef. J Agric Food Chem 2005; 53(12):4736-9.
[19.] Everaert I, Taes Y, De Heer E, Baelde H, Zutinic A, Yard B, et al. Low plasma carnosinase activity promotes carnosinemia after carnosine ingestion in humans. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2012; 302(12):F1537-44.
[20.] Archer J. Effect of AB070597 on blood-serum creatinine concentration in cats with chronic kidney disease. Research Journal for Veterinary Practitioners 2015; 3(3):58-68.
[21.] Archer J. Effect of amino acid and peptide complex AB070597 on renal function in dogs with chronic kidney disease. International Animal Health Journal 2018; 5(2):38-42.
[22.] Goldstein RE, Marks SL, Cowgill LD, Kass PH, Rogers QR. Plasma amino acid profiles in cats with naturally acquired chronic renal failure. Am J Vet Res 1999; 60(1):109-13.
[23.] Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 2009; 150(9):604-12.
[24.] Tsai CW, Ting IW, Yeh HC, Kuo CC. Longitudinal change in estimated GFR among CKD patients: A 10-year follow-up study of an integrated kidney disease care program in Taiwan. PLoS One 2017; 12(4):e0173843.
[25.] Tukey JW. Exploratory Data Analysis, first ed., Addison -Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts, 1977.
[26.] Nijveldt RJ, Van Leeuwen PA, Van Guldener C, Stehouwer CD, Rauwerda JA, Teerlink T. (2002) Net renal extraction of asymmetrical (ADMA) and symmetrical (SDMA) dimethylarginine in fasting humans. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17(11):1999-2002.
[27.] Bode-Boger SM, Scalera F, Kielstein JT, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Breithardt G, Fobker M, et al. Symmetrical dimethylarginine: a new combined parameter for renal function and extent of coronary artery disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17(4):1128-34.
[28.] Zoccali C, Bode-Boger S, Mallamaci F, Benedetto F, Tripepi G, Malatino L, et al. Plasma concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease: a prospective study. Lancet 2001; 358(9299):2113-7.
[29.] Klahr S. Can L-arginine manipulation reduce renal disease? Semin Nephrol 1999; 19(3):304-9.
[30.] Thomsen K, Nielsen CB, Flyvbjerg A. Effects of glycine on glomerular filtration rate and segmental tubular handling of sodium in conscious rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2002; 29(5-6):449-54.
[31.] Yatzidis H (2002). A new, superior, single and stable, amino acid and bicarbonate-based glucose-free solution for peritoneal dialysis. Dialysis and Transplantation 2002; 31:143-149.
[32.] Varnier M, Leese GP, Thompson J, Rennie MJ. Stimulatory effect of glutamine on glycogen accumulation in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 1995; 269(2 Pt 1):E309-15.
[33.] Kopple JD, Swendseid ME. Evidence that histidine is an essential amino acid in normal and chronically uremic man. J Clin Invest 1975; 55(5):881-91.